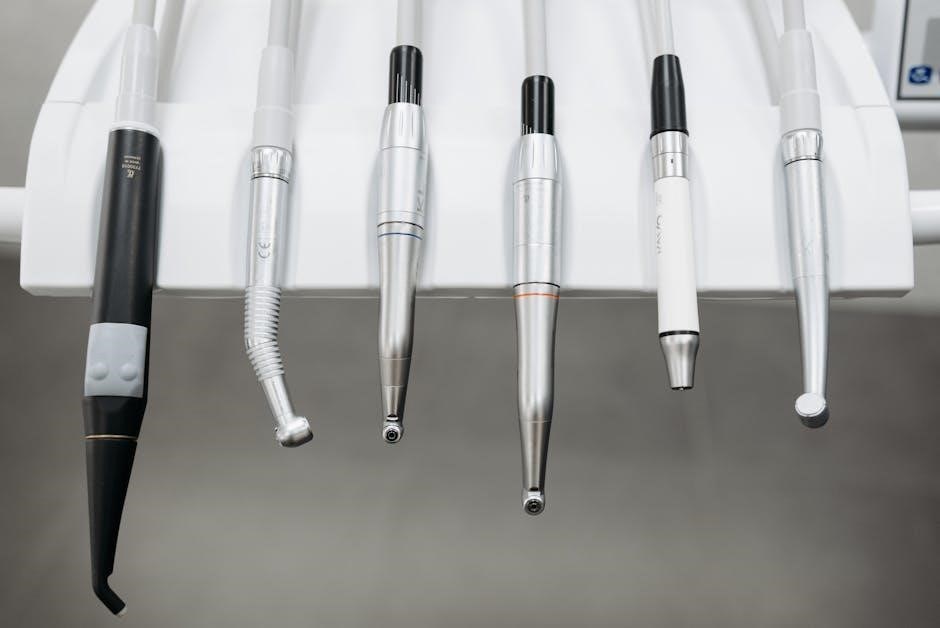
dental instruments pictures and names pdf
Basic Dental Instruments
Essential tools include dental trays for organizing instruments, dental mirrors for visibility, probes for measuring, and explorers for detecting issues. These instruments are fundamental for diagnostics and procedures.
1.1 Dental Tray
A dental tray is a essential tool used to organize and hold instruments during procedures. It comes in various designs, including disposable and stainless steel options, to suit different needs. Its purpose is to provide a clean, specific area for instruments, ensuring efficiency and organization in dental exams and treatments.
1.2 Dental Mirror
A dental mirror is a handheld device with a reflective surface, used to enhance visibility and access during dental procedures. It allows dentists to view areas difficult to see directly. Available in various sizes, it is an indispensable tool for examining oral cavities, ensuring precise diagnostics and effective treatment planning.
1.3 Dental Probes
Dental probes are calibrated instruments used to measure pocket depths and detect abnormalities in teeth and gums. They are essential for periodontal assessments and diagnosing conditions like caries or fractures. Available in various types, such as periodontal probes, they provide precise measurements, aiding in effective treatment planning and preventive care. Their accuracy ensures early detection of oral health issues.
1.4 Dental Explorers
Dental explorers are sharp, pointed instruments used to detect caries, fractures, or calculus. They come in different types, such as the 11/12 explorer, designed for specific oral areas. Explorers help identify abnormalities by gently probing surfaces, ensuring accurate diagnoses. Regular use aids in early detection of dental issues, promoting preventive care and maintaining oral health effectively.
Surgical Dental Instruments
Surgical knives and bone mills are essential for precise tissue removal and shaping. Titanium mesh is used for reconstruction, ensuring durability and compatibility. These tools enhance surgical outcomes.
2.1 Surgical Knives
Surgical knives are precision tools used in dental procedures for incisions and tissue removal. They feature sharp, sterile blades made from high-grade stainless steel. Designed for accuracy, they come in various sizes and shapes to suit specific surgical needs. Proper sterilization is crucial to prevent infection. Their ergonomic handles ensure a firm grip, enhancing control during delicate operations.
2.2 Bone Mills
Bone mills are specialized instruments used to prepare and shape bone grafts during dental surgeries. They are designed to efficiently grind and contour bone material for optimal fit and integration. Available in various sizes, bone mills ensure precise tissue preparation, promoting successful grafting outcomes. Their durability and ergonomic design make them essential for surgical bone reconstruction procedures in modern dentistry.
2.3 Titanium Mesh
Titanium mesh is a biocompatible, flexible grid used in dental surgeries for bone reconstruction and augmentation. It supports bone regeneration and provides structural stability. Often used in implant dentistry, it aids in creating a stable environment for implants. Its flexibility allows customization to fit specific anatomical needs, making it a versatile tool in both dental and broader medical applications for tissue repair and reconstruction.

Hygiene Dental Instruments
Precision tips and explorers are key hygiene tools, ensuring effective cleaning and examination. Made from durable materials like stainless steel, they maintain sharp edges for precise dental care procedures.
3.1 Precision Tips
Precision tips are crafted with 440A stainless steel and SmartSharp Technology, ensuring sharp, well-defined edges. These tips are essential for precise dental hygiene procedures, offering durability and effectiveness in cleaning and examining teeth. Their design enhances accuracy, making them indispensable in modern dental care for both routine and complex treatments.
3.2 Sterilization Procedures
Sterilization is critical for infection control. Instruments must be cleaned before sterilization, using methods like steam autoclaves or chemical solutions. Proper protocols ensure all tools are disinfected and safe for reuse. Regular sterilization maintains hygiene standards and prevents contamination, essential for patient safety and effective dental care.
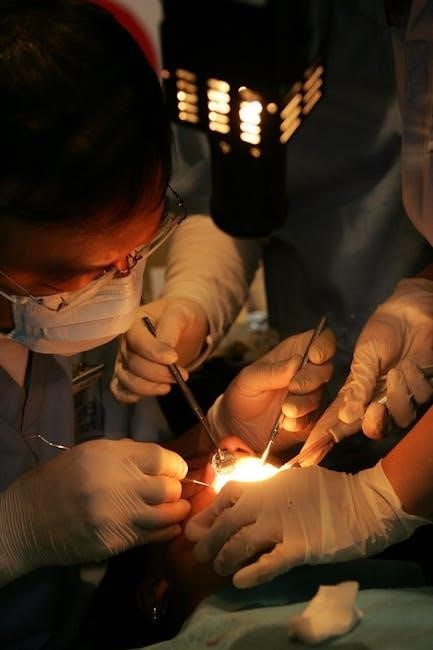
Implant Dentistry Instruments
Key instruments include implant drills for precise bone preparation, implant drivers for placing implants, and healing abutments to support tissue recovery post-surgery.
4.1 Implant Drills
Implant drills are used to prepare the bone site for dental implants. They come in various sizes and are designed for precise, controlled drilling to ensure proper fit and alignment. These drills are typically sterilized and used in surgical procedures to create the exact diameter and depth needed for implant placement, ensuring optimal osseointegration and stability.
4.2 Implant Drivers
Implant drivers are essential for seating and tightening dental implants. They come in various sizes to match specific implant systems, ensuring a secure fit. These instruments are used to apply precise torque, preventing damage to the implant or surrounding tissue. Proper use of drivers is crucial for achieving stability and long-term success of the implant.
4.3 Healing Abutments
Healing abutments are temporary components used during the healing phase after implant placement. They protect the implant site, promoting gingival healing and shaping the soft tissue. Available in various heights and sizes, these abutments are designed to minimize discomfort and prepare the site for the final prosthesis, ensuring a smooth transition to the restorative phase.
Restorative Dental Instruments
Key tools include filling instruments for shaping and packing materials, and dental burs for preparing tooth surfaces. These instruments are crucial for repairing and restoring teeth effectively.
5.1 Filling Instruments
Filling instruments are designed for precise shaping and packing of dental materials like amalgam or composite. They include condensers, plugs, and burnishers. These tools ensure proper adaptation and smoothing of restorative materials, enhancing durability and aesthetics. Proper selection and use are vital for successful restorations, as outlined in detailed PDF guides with images.
5.2 Dental Burs
Dental burs are precision cutting tools used for shaping and removing tooth structures. Available in materials like diamond, carbide, and stainless steel, they are classified by shape, size, and grit. Each type serves specific purposes, from cavity preparation to enamel shaping. Detailed in PDF guides, their images and names help dentists select the right bur for procedures, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in restorative work.
Orthodontic Instruments
Orthodontic instruments include pliers for bending wires, arch wires for aligning teeth, and ligature cutters for securing brackets. These tools are essential for precise adjustments in orthodontic treatments and are detailed in PDF guides with images and names for easy identification.
6.1 Orthodontic Pliers
Orthodontic pliers are specialized tools used to bend and shape wires, secure brackets, and tighten or loosen orthodontic appliances. They come in various types, such as needle-nose pliers and curved pliers, each designed for specific tasks. PDF guides provide detailed images and names of these instruments, helping professionals identify and use them effectively in orthodontic treatments.
6.2 Arch Wires
Arch wires are crucial in orthodontics for applying force to teeth, guiding them into proper alignment. Made from materials like stainless steel, nickel-titanium, or beta-titanium, they vary in flexibility and strength. PDF guides provide detailed images and names of arch wires, helping professionals identify and select the appropriate wire for specific orthodontic cases and treatment stages.
Diagnostic Instruments
Digital sensors capture detailed tooth images, replacing traditional X-rays, while panoramic X-ray machines provide wide-angle views for comprehensive diagnostics, both essential for accurate patient assessments and treatment planning.
7.1 Digital Sensors
Digital sensors are modern diagnostic tools placed inside the mouth to capture high-resolution images of teeth and surrounding tissues. They replace traditional X-ray films, offering instant results, reduced radiation exposure, and enhanced accuracy for dental professionals. These sensors are durable, reusable, and come in various sizes to accommodate different patient needs and anatomical requirements.
7.2 Panoramic X-ray Machines
Panoramic X-ray machines provide wide-angle views of the upper and lower jaw in a single image. They are used to diagnose issues like impacted teeth, fractures, or tumors. These machines capture detailed visuals of dental structures, aiding in comprehensive treatment planning. They are essential for orthodontic assessments and surgical procedures, offering a broader perspective than traditional X-rays.
Classification of Dental Instruments
G.V. Black classified instruments into ORDER, SUBORDER, CLASS, and SUBCLASS. This system organizes tools by purpose, aiding in identification and standardization, with examples like dental trays and probes.
8.1 G.V. Black Classification
G.V. Black developed a systematic classification of dental instruments into ORDER, SUBORDER, CLASS, and SUBCLASS. This framework organizes tools by purpose, simplifying identification and standardization. Examples include dental trays and probes, categorized based on their functions and designs. This classification aids in understanding the role of each instrument, enhancing efficiency in dental procedures and education.

Photography and Imaging
Digital sensors capture high-quality images of teeth, replacing traditional X-ray films. These tools enhance diagnostic accuracy and are essential for modern dental imaging and documentation processes.
9.1 Capturing Dental Instrument Images
Capturing clear images of dental instruments is crucial for documentation and education. High-quality photos are used in PDF guides and online catalogs, ensuring accurate identification. Proper lighting and angles enhance detail, making instruments easily recognizable. These images are essential for training and reference, helping professionals understand each tool’s purpose and design. Digital sensors and advanced photography techniques ensure precision and clarity in capturing these images.
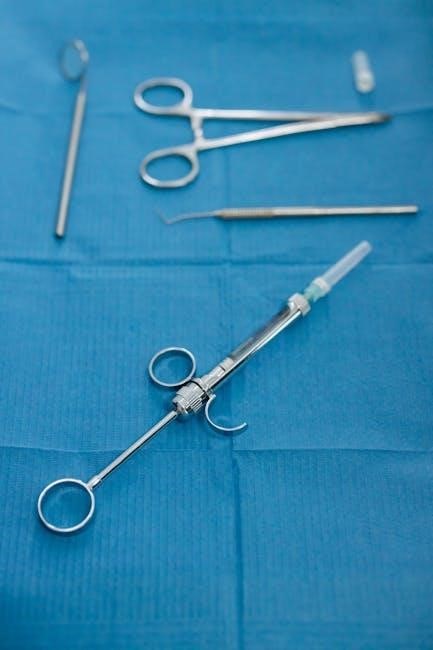
Resources and Guides
PDF guides and online catalogs provide comprehensive overviews of dental instruments, including names and images. These resources are essential for education and quick reference, aiding in instrument identification and understanding their functions.
10.1 PDF Guides for Dental Instruments
PDF guides offer comprehensive overviews of dental instruments, featuring detailed names and images. These resources are designed for educational purposes, providing clear visuals and descriptions of each tool’s function. They serve as invaluable references for dental professionals, aiding in instrument identification and understanding their roles in various procedures. These guides are widely accessible and support continuous learning in dentistry.
10.2 Online Catalogs for Dental Tools
Online catalogs provide detailed listings of dental tools, featuring names, images, and functional descriptions. These platforms allow users to search, compare, and purchase instruments efficiently. Many catalogs offer filters for size, material, and brand, making it easier to find specific tools. They also include information on sterilization and maintenance, supporting dental professionals in making informed decisions.